Exporting data frames into nice tables
The export_table() functions creates nicely formatted
tables in text, markdown or HTML format. You can add (coloured) captions
or footer lines to the table as well, and you can even create multiple
tables from a list of data frames.
This vignette shows some examples how to do this (focusing on text
output). Note that export_table() returns a formatted
string, which prints nicely (which essentially just uses
cat()).
Note: The vignettes includes example with coloured text output. The coloured text is not rendered in this vignette. Rather, try out these examples and look at the results in your console!
library(insight)
x <- iris[1:3, c(1, 2, 5)]
# the table as "readable" output
export_table(x)
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
# see the underlying string
unclass(export_table(x))
#> [1] "Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species\n------------------------------------\n 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa\n 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa\n 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa\n"Adding (coloured) titles
A title can be added by either using the caption
argument, or by adding a string as table_caption
attribute.
# a simple caption
export_table(x, caption = "Title")
#> Title
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
# we use a new object, so "x" has no attributes yet
out <- x
attr(out, "table_caption") <- "Another title"
export_table(out)
#> Another title
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosacaption can also be character vector of length 2, with
the first element being the caption, and the second being the name of a
colour (see ?print_colour for available options). This is
helpful for printing coloured table captions.
# A red caption
export_table(x, caption = c("# Title", "red"))
#> # Title
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
# same for attribute
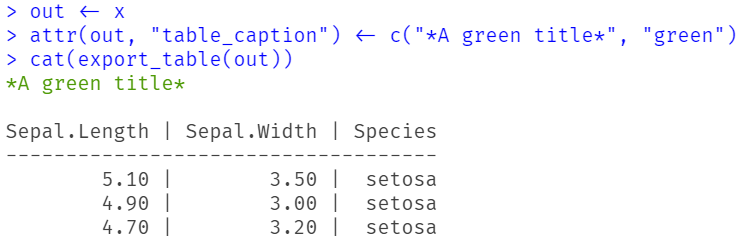
out <- x
attr(out, "table_caption") <- c("*A green title*", "green")
export_table(out)
#> *A green title*
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosaSince the coloured text is not rendered, we provide a screenshot as example here:
Adding (coloured) table footers
Use the footer argument to add a footer line to the
table. It is also possible to add a string as table_footer
attribute.
# colored caption, simple footer
export_table(
x,
caption = c("# Title", "red"),
footer = "Footer line"
)
#> # Title
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line
# as attribute
out <- x
attr(out, "table_caption") <- c("*A green title*", "green")
attr(out, "table_footer") <- "A simple footer"
export_table(out)
#> *A green title*
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> A simple footerColoured footers can be added in the same way as for captions.
# colored caption and footer
export_table(
x,
caption = c("# Title", "red"),
footer = c("Footer line in blue", "blue")
)
#> # Title
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line in blue
# as attribute
out <- x
attr(out, "table_caption") <- c("*A green title*", "green")
attr(out, "table_footer") <- c("Footer line in blue", "blue")
export_table(out)
#> *A green title*
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line in blueAdding subtitles
Subtitles can be added using the subtitle argument, or
the table_subtitle attribute. Note that you must take care
of adding new-line characters.
# colored caption, subtitle and footer
export_table(
x,
caption = c("# Title", "red"),
subtitle = c("\n A subtitle in yellow", "yellow"),
footer = c("Footer line in blue", "blue")
)
#> # Title
#> A subtitle in yellow
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line in blue
# as attribute
out <- x
attr(out, "table_caption") <- c("*A green title*", "green")
attr(out, "table_subtitle") <- c("\nA yellow subtitle", "yellow")
attr(out, "table_footer") <- c("Footer line in blue", "blue")
export_table(out)
#> *A green title*
#> A yellow subtitle
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line in blueExporting multiple data frames into multiple tables
Multiple data frames saved in a list() can be used to
create multiple tables at once.
x <- list(
data.frame(iris[1:3, c(1, 2, 5)]),
data.frame(iris[51:53, c(1, 3, 5)]),
data.frame(iris[111:113, c(1, 4, 5)])
)
# three different tables
export_table(x)
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginicaAdding table captions and footers
For multiple tables, it is also possible to add a caption for each
table. Simply use a list() of strings for the
caption argument, or add a table_caption
attribute. to each data frame in the list.
# one caption for each table
export_table(x, caption = list("Table 1", "Table 2", "Table 3"))
#> Table 1
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#>
#> Table 2
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#>
#> Table 3
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginica
# add attribute to *each* data frame
out <- x
for (i in seq_along(out)) {
attr(out[[i]], "table_caption") <- paste("Table", i)
}
export_table(out)
#> Table 1
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#>
#> Table 2
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#>
#> Table 3
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginicaIn the same way you can add multiple footers. Note, however, that you have to take care about adding new-line characters.
# add captions and footers for each table
export_table(
x,
caption = list("Table 1", "Table 2", "Table 3"),
footer = list("Footer 1\n\n", "Footer 2\n\n", "Footer 3\n\n")
)
#> Table 1
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer 1
#>
#>
#> Table 2
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#> Footer 2
#>
#>
#> Table 3
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginica
#> Footer 3
out <- x
for (i in seq_along(out)) {
attr(out[[i]], "table_caption") <- paste("Table", i)
attr(out[[i]], "table_footer") <- paste("Footer", i, "\n\n")
}
export_table(out)
#> Table 1
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer 1
#>
#>
#> Table 2
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#> Footer 2
#>
#>
#> Table 3
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginica
#> Footer 3Finally, you can even add multiple footer lines to each table, giving each a different color. In this case, each list element has to be a character vector of length 2 (the first element being the caption, and the second being the name of a colour).
# Colored table captions and multiple footers per table
export_table(
x,
caption = list(
c("Red Table 1", "red"),
c("Blue Table 2", "blue"),
c("Green Table 3", "green")
),
footer = list(
list(c("Footer line 1\n", "green"), c("Second line\n\n", "red")),
list(c("Footer line A\n", "blue"), c("Second line\n\n", "green")),
list(c("Footer line I\n", "yellow"), c("Second line\n\n", "blue"))
)
)
#> Red Table 1
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Species
#> ------------------------------------
#> 5.10 | 3.50 | setosa
#> 4.90 | 3.00 | setosa
#> 4.70 | 3.20 | setosa
#> Footer line 1
#> Second line
#>
#>
#> Blue Table 2
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Length | Species
#> ----------------------------------------
#> 7.00 | 4.70 | versicolor
#> 6.40 | 4.50 | versicolor
#> 6.90 | 4.90 | versicolor
#> Footer line A
#> Second line
#>
#>
#> Green Table 3
#>
#> Sepal.Length | Petal.Width | Species
#> --------------------------------------
#> 6.50 | 2.00 | virginica
#> 6.40 | 1.90 | virginica
#> 6.80 | 2.10 | virginica
#> Footer line I
#> Second lineSplitting one long table into multiple tables
When the table is wider than the current width (i.e. line length) of
the console (or any other source for textual output, like markdown
files), the table can be split into multiple parts to fit the width of
the screen using the table_width argument. This is set to
"auto" by default, i.e. by default tables are always
adjusted to fit into the current display.
We’ll demonstrate this using a codebook of a dataset from the datawizard package.
data(efc, package = "datawizard")
# prepare a data set, in this example a codebook of the EFC dataset
out <- datawizard::data_codebook(efc[, 1:3])
out$.row_id <- NULL
export_table(
out,
table_width = 70, # fix width to 70 chars
empty_line = "-", # empty lines (separator rows) indicated by "-"
cross = "+" # use "+" where vertical and horizontal table lines cross
)
#> ID | Name | Label | Type
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 1 | c12hour | average number of hours of care per week | numeric
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 2 | e16sex | elder's gender | numeric
#> | | |
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 3 | e42dep | elder's dependency | categorical
#> | | |
#> | | |
#> | | |
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#>
#> ID | Missings | Values | Value Labels | N | Prop
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 1 | 2 (2.0%) | [5, 168] | | 98 |
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | male | 46 | 46.0%
#> | | 2 | female | 54 | 54.0%
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 3 | 3 (3.0%) | 1 | independent | 2 | 2.1%
#> | | 2 | slightly dependent | 4 | 4.1%
#> | | 3 | moderately dependent | 28 | 28.9%
#> | | 4 | severely dependent | 63 | 64.9%
#> ------------------------------------------------------------As you can see, the third row in the first table part contains some
empty rows. This is because the height of the tables are always the same
by default, to avoid confusion. However, it is also possible to remove
redundant empty rows, using the remove_duplicates
argument.
export_table(
out,
table_width = 70,
empty_line = "-",
cross = "+",
remove_duplicates = TRUE
)
#> ID | Name | Label | Type
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 1 | c12hour | average number of hours of care per week | numeric
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 2 | e16sex | elder's gender | numeric
#> ---+---------+------------------------------------------+------------
#> 3 | e42dep | elder's dependency | categorical
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------------
#>
#> ID | Missings | Values | Value Labels | N | Prop
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 1 | 2 (2.0%) | [5, 168] | | 98 |
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | male | 46 | 46.0%
#> | | 2 | female | 54 | 54.0%
#> ---+----------+----------+----------------------+----+------
#> 3 | 3 (3.0%) | 1 | independent | 2 | 2.1%
#> | | 2 | slightly dependent | 4 | 4.1%
#> | | 3 | moderately dependent | 28 | 28.9%
#> | | 4 | severely dependent | 63 | 64.9%
#> ------------------------------------------------------------